From Chat to Orchestration
The utility of AI has expanded far beyond simple question-and-answer interactions. The true power of modern Large Language Models (LLMs) lies in orchestration—the ability to plan, execute, and manage complex, multi-step workflows autonomously.
We are transitioning from using AI as a consultant to deploying AI as a workforce.
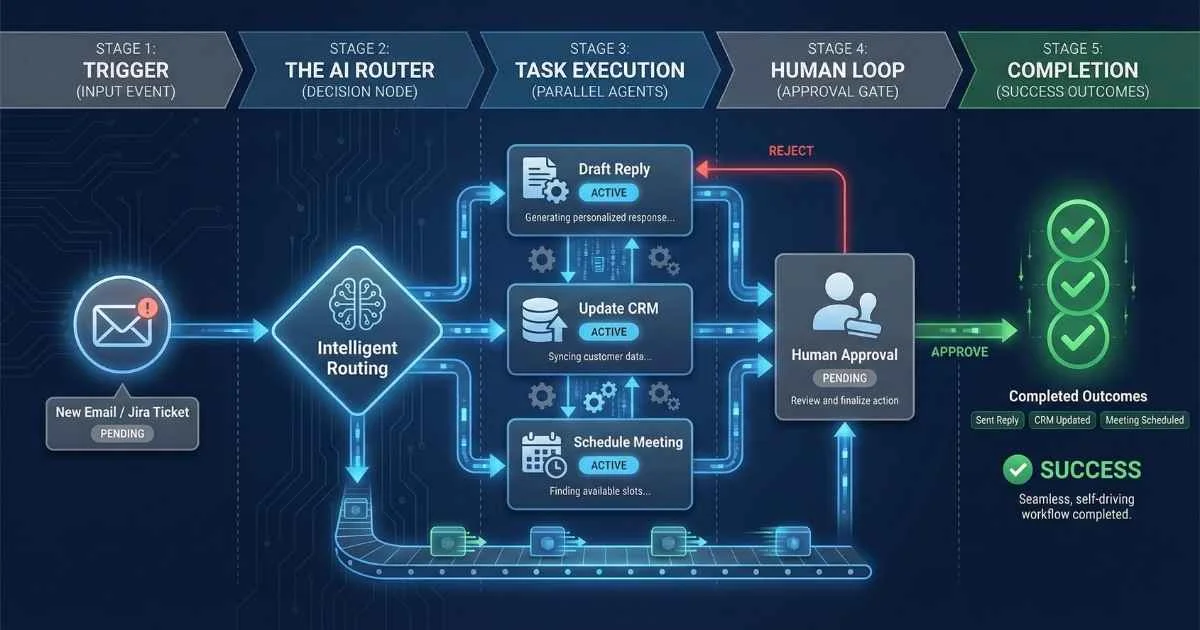
Agentic automation allows developers to chain multiple AI systems together, where one agent’s output becomes another’s input. An agent can research a topic, pass the findings to a writer agent, who then hands off a draft to a review agent—all without human intervention.
Welcome to the era of agentic AI workflows. In December 2025, the tools have matured, the standards have emerged, and the gap between businesses that embrace this technology and those that don’t is widening rapidly.
Consider these numbers from December 2025:
- 88% of organizations now use AI regularly in at least one business function—up from 78% last year (McKinsey State of AI 2025)
- 75% of firms are actively using AI-driven workflow automation, with visible productivity gains within six months (Flowster 2025)
- 8x increase in weekly ChatGPT Enterprise messages over the past year, with structured workflows (Projects, Custom GPTs) seeing 19x growth (OpenAI Enterprise Report 2025)
- 40-60 minutes saved daily by enterprise AI users—heavy users save 10+ hours weekly (OpenAI Enterprise Report 2025)
This guide will take you from “I’ve heard of workflow automation” to “I’ve built my own AI-powered system.” Let’s dive in.
92%
Execs Planning AI Automation
40-60m
Daily Time Savings
74%
ROI in Year 1
75%
Report Improved Output
Sources: Flowster • OpenAI Enterprise • Google Research
What You’ll Learn
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand:
- How agentic AI differs from traditional automation — and why it matters
- Building with modern frameworks — LangChain 1.0, LangGraph 1.0, CrewAI
- Leveraging no-code platforms — Zapier Agents, n8n 2.0, Activepieces
- Creating custom AI assistants — Custom GPTs vs Claude Projects
- The MCP revolution — The new “USB-C for AI” standard
- Measuring and maximizing ROI — With December 2025 benchmarks
- Production best practices — Security, reliability, and observability
Let’s start with the fundamental shift that’s happening right now.
Understanding Agentic AI: Beyond Simple Automation
What Makes Automation “Agentic”?
I used to think automation was about connecting apps: “When I get an email with an attachment, save it to Dropbox.” That’s Level 1 automation. Useful, but rigid.
Agentic AI is fundamentally different. It’s AI that can think, adapt, and act on your behalf.
Here’s the simplest way I can explain it:
Traditional Automation = A vending machine. Fixed buttons → fixed outputs. No decisions involved.
AI-Enhanced Automation = A smart speaker. It understands your request, but follows a script.
Agentic AI = A capable assistant. You give them a goal, they figure out how to achieve it, and they adjust when things change.
For a deeper dive into how agentic AI is transforming software development, see the AI Agents guide.
The key capabilities that make AI “agentic”:
| Capability | What It Means | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Makes decisions to achieve stated goals | ”Find the best approach, then execute it” |
| Reasoning | Breaks complex tasks into manageable subtasks | ”This requires research, then analysis, then writing” |
| Adaptability | Adjusts when things change or fail | ”API is down? Let me try a different data source” |
| Tool Use | Invokes external services and APIs | ”I’ll search Google Scholar, update Notion, then notify via Slack” |
| Memory | Maintains context across interactions | ”You mentioned last week that you prefer concise reports” |
The Automation Spectrum: Where Do You Fit?
Most organizations are stuck at Level 2 or 3. Here’s how I think about the five levels:
| Level | Type | Capability | Example | Your Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rule-Based | Fixed If-Then rules | Email auto-forwarding | 🟢 Everyone |
| 2 | Templated AI | AI + fixed prompts | Auto-summarize emails | 🟢 Most teams |
| 3 | Dynamic AI | AI with context awareness | Smart email drafting | 🟡 Early adopters |
| 4 | Single Agent | Autonomous task completion | Research + draft report | 🟠 Leaders |
| 5 | Multi-Agent | Coordinated agent teams | Full project execution | 🔴 Cutting edge |
The good news? The tools to jump to Level 4 or 5 are now accessible—and this guide shows you how.
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#4f46e5', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#3730a3', 'lineColor': '#6366f1', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart LR
A["Level 1:\nRule-Based"] --> B["Level 2:\nAI-Enhanced"]
B --> C["Level 3:\nDynamic AI"]
C --> D["Level 4:\nSingle Agent"]
D --> E["Level 5:\nMulti-Agent"]
style A fill:#ffd6d6
style B fill:#ffe4b5
style C fill:#fffacd
style D fill:#d4edda
style E fill:#cce5ffTry This Yourself: The “Coffee Test”
Here’s a quick way to understand agentic AI:
Level 2 Automation: “When it’s 8 AM, remind me to make coffee.”
Level 4 Agentic AI: “Make sure I have coffee when I need it.”
The agentic system might:
- Learn that you usually want coffee at 8 AM on weekdays, 9 AM on weekends
- Check your calendar—if you have an early meeting, adjust the timing
- Notice you’re working late and offer evening coffee
- Order more beans when running low
- Skip the reminder if you’re already drinking something
That’s the difference between “follow a rule” and “achieve a goal.”
The December 2025 Tipping Point
Something historic happened on December 9, 2025: The Linux Foundation announced the Agentic AI Foundation (AAIF), with Anthropic’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) as a foundational contribution.
The founding members read like a who’s-who of AI:
- Co-founders: Anthropic, Block, OpenAI
- Platinum members: Amazon Web Services, Bloomberg, Cloudflare, Google, Microsoft
- Additional projects: Block’s “goose” agent framework, OpenAI’s “AGENTS.md” standard
Why does this matter? It signals that the major players are aligning on open standards. The infrastructure for agentic AI is becoming universal—not fragmented by vendor lock-in.
🎯 What this means for you: The tools you learn today will work with the broader ecosystem tomorrow. We’re past the “which vendor will win?” phase. Now it’s about building.
The Modern AI Workflow Stack (December 2025)
Before we dive into specific tools, let me map out the landscape. Think of this as a layered architecture, from foundation to interface:
Layer 1: Foundation Models
The brains of the operation. As of December 2025:
| Model | Release | Strengths | Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-5.2 | Dec 11, 2025 | Agentic tool-calling, best general reasoning, enhanced vision | 400K tokens |
| GPT-5.2-Codex | Dec 18, 2025 | Agentic coding specialist, Windows support, security | 400K tokens |
| Claude Opus 4.5 | Nov 24, 2025 | World’s best coding model, SWE-bench 80.9%, computer use | 200K tokens |
| Gemini 3 Pro | Nov 2025 | Deep Research Agent, native multimodal, agentic coding | 1M+ tokens |
| Gemini 3 Flash | Dec 2025 | Frontier speed, PhD-level reasoning, multimodal | 1M+ tokens |
| LLaMA 4 Maverick | Apr 2025 | Open-source, local running, 10M token context | 10M tokens |
Layer 2: Agent Frameworks
The orchestration layer that coordinates AI reasoning with tool use:
- LangChain 1.0 (October 2025): Production-ready, modular architecture
- LangGraph 1.0 (October 2025): Graph-based stateful workflows
- CrewAI: Role-based multi-agent teams
- Dify (v1.11.2, Dec 2025): Open-source with visual builder, RAG engine, Knowledge Pipeline, and Queue-based Graph Engine. Winner of 2025 AWS Partner Award.
- Flowise: Visual LangChain builder (acquired by Workday in 2025)
- LangFlow: Drag-and-drop for rapid prototyping
Layer 3: Automation Platforms
Where AI meets your business tools:
- Zapier: 8,000+ integrations, AI Agents, Canvas, MCP support
- n8n 2.0 (December 15, 2025): 70+ AI nodes, self-hosted option
- Activepieces: Open-source, 400+ MCP servers
- Microsoft Copilot Studio: Enterprise AI agents, M365 integration
Layer 4: Custom AI Interfaces
Personalized AI assistants without code:
- Custom GPTs: No-code ChatGPT customization
- Claude Projects: Persistent workspaces with knowledge bases
- Google Gems: Custom Gemini personalities
Layer 5: Integration Standards
The glue that makes everything work together:
- MCP (Model Context Protocol): Universal AI-to-tool connector
- OpenAI Function Calling: Structured tool invocation
- Anthropic Tool Use: Claude’s action layer
Agent Framework Comparison
December 2025 ecosystem overview
| Framework | Type | Best For | Difficulty | GitHub ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
LangChain 1.0 | Full Framework | Sequential workflows | Medium | 97K+ |
LangGraph 1.0 | Graph Orchestration | Stateful multi-agent | Medium | 15K+ |
CrewAI | Role-Based Teams | Business workflows | Easy | 23K+ |
Dify 2.0 | No-Code Platform | Production apps | Easy | 52K+ |
Flowise | Visual Builder | Enterprise | Easy | 32K+ |
LangFlow | Drag-and-Drop | Rapid prototyping | Easy | 35K+ |
💡 October 2025: Both LangChain 1.0 and LangGraph 1.0 reached stable release, marking production-ready status for enterprise deployments.
Building with Agent Frameworks
Let me walk you through the major frameworks and when to use each. Think of these as different tools in your workshop—each excels at different jobs.
LangChain 1.0 & LangGraph 1.0: The Dynamic Duo
These two reached stable 1.0 releases in October 2025, with LangChain 1.1.0 on December 1, 2025 and LangChain 1.2.0 on December 15, 2025. The 1.2.0 release added simplified provider-specific tool parameters and a rewritten Google GenAI integration using Google’s consolidated Generative AI SDK.
LangChain 1.0 is your go-to for:
- Sequential, modular workflows
- Standard tool-calling patterns with the new
create_agentAPI - Production-ready middleware for context engineering, dynamic prompts, and guardrails
- When you need reliable, predictable behavior
LangGraph 1.0 extends LangChain for:
- Complex state management with graph-based architecture
- Loops and conditional branching
- Human-in-the-loop approval steps (built-in)
- Multi-agent coordination
- Durable execution that survives crashes and restarts
- When workflows need to adapt dynamically
💡 Analogy: Think of LangChain as a recipe—steps executed in order. LangGraph is a choose-your-own-adventure book—paths branch based on what happens.
Here’s a simple decision matrix:
| Scenario | LangChain | LangGraph |
|---|---|---|
| Simple chatbot | ✅ Best | Overkill |
| Sequential pipeline | ✅ Best | Optional |
| Branching logic | Limited | ✅ Best |
| Multi-agent coordination | Difficult | ✅ Best |
| Human approval steps | Manual | ✅ Built-in |
| Production agents | Good | ✅ Best |
Source: LangChain Official Documentation (December 2025)
⚠️ Security Alert (December 25, 2025): A critical serialization injection vulnerability (CVE-2025-68664, codenamed “LangGrinch”) was disclosed in
langchain-coreversions prior to 1.2.5 and 0.3.81. This flaw could allow secret theft and prompt injection. Update to versions 1.2.5+ or 0.3.81+ immediately. (The Hacker News)
CrewAI: Role-Based Multi-Agent Teams
This is my favorite for business workflows. CrewAI treats agents like team members:
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#4f46e5', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#3730a3', 'lineColor': '#6366f1', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart TB
A["User Request"] --> B["Manager Agent"]
B --> C["Research Agent"]
B --> D["Analysis Agent"]
B --> E["Writing Agent"]
C --> F["Gather Sources"]
F --> G["Synthesize Findings"]
D --> G
G --> H["Draft Report"]
E --> H
H --> I["Quality Review"]
I --> J["Final Output"]Key features in December 2025:
- Role-Based Agents: Each agent has defined responsibilities, goals, and backstories
- Flows: Sequential, parallel, and conditional processing
- Memory System: Context maintained across conversations
- Async Support: CrewAI 1.7.0 (December 8, 2025) added full async support for flows, crews, tasks, and tools
- Scale: CrewAI ran 1.1 billion agentic automations in Q3 2025
When to use CrewAI: Business workflows requiring predictable, reliable automation. Think sales research, content pipelines, or customer analysis.
💡 Analogy: If LangGraph is a conductor coordinating an orchestra, CrewAI is a team manager assigning tasks to specialists.
CrewAI vs AutoGen: Quick Comparison
| Aspect | CrewAI | AutoGen |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Curve | Easier | Steeper |
| Agent Model | Role-based teams | Conversational agents |
| Best For | Business workflows | Research/experimentation |
| Code Execution | Plugin | Built-in sandbox |
| December 2025 Status | v1.7.0, active development | v0.4, limited maintenance* |
| Enterprise Features | AOP platform launched Nov 2025 | Limited |
*Note: Microsoft is shifting focus to a new “Agent Framework” (Sources: CrewAI GitHub, Microsoft AutoGen)
Multi-Agent Architecture Patterns
When building systems with multiple AI agents, choosing the right architecture is critical. Here are the five most common patterns:
Pattern 1: Hierarchical (Manager-Worker)
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#4f46e5', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#3730a3', 'lineColor': '#6366f1', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart TD
U[User Request] --> M[Manager Agent]
M --> W1[Research Worker]
M --> W2[Analysis Worker]
M --> W3[Writing Worker]
W1 --> M
W2 --> M
W3 --> M
M --> O[Final Output]| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Best For | Structured workflows with clear task delegation |
| Examples | Content production, research projects, customer support escalation |
| Pros | Clear accountability, easy to debug, predictable flow |
| Cons | Manager can become bottleneck, single point of failure |
| Tools | CrewAI (hierarchical process), LangGraph with supervisor |
Pattern 2: Peer-to-Peer (Collaborative)
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#10b981', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#059669', 'lineColor': '#34d399', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart LR
A1[Critic Agent] <--> A2[Generator Agent]
A2 <--> A3[Refiner Agent]
A3 <--> A1| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Best For | Creative tasks requiring iteration and diverse perspectives |
| Examples | Brainstorming, design review, code review with multiple reviewers |
| Pros | Emergent creativity, parallel perspectives, self-improving |
| Cons | Hard to control, may diverge or loop, higher token costs |
| Tools | AutoGen conversation patterns, custom LangGraph graphs |
Pattern 3: Pipeline (Sequential)
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#f59e0b', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#d97706', 'lineColor': '#fbbf24', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart LR
A1[Ingest Agent] --> A2[Process Agent]
A2 --> A3[Analyze Agent]
A3 --> A4[Format Agent]
A4 --> A5[Deliver Agent]| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Best For | Data processing, document workflows, ETL operations |
| Examples | Report generation, email processing, content repurposing |
| Pros | Predictable, easy to monitor, clear stages |
| Cons | No parallelism, slowest stage determines throughput |
| Tools | LangChain sequential chains, n8n workflows, CrewAI sequential process |
Pattern 4: Specialist Pool (Router)
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#8b5cf6', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#7c3aed', 'lineColor': '#a78bfa', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart TD
I[Input] --> R[Router Agent]
R -->|Code question| S1[Code Specialist]
R -->|Data question| S2[Data Specialist]
R -->|Writing task| S3[Writing Specialist]
R -->|General| S4[Generalist]
S1 --> O[Output]
S2 --> O
S3 --> O
S4 --> O| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Best For | Dynamic task routing based on content type |
| Examples | Customer support triage, code review by language, multi-domain Q&A |
| Pros | Optimal expertise matching, efficient resource use |
| Cons | Routing logic complexity, classifier errors |
| Tools | LangGraph with conditional edges, n8n Switch node, Zapier Paths |
Pattern 5: Debate/Consensus
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#ef4444', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#dc2626', 'lineColor': '#f87171', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart TD
Q[Question] --> A1[Perspective A]
Q --> A2[Perspective B]
Q --> A3[Perspective C]
A1 --> J[Judge Agent]
A2 --> J
A3 --> J
J --> D[Final Decision]| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Best For | High-stakes decisions requiring verification |
| Examples | Medical diagnosis support, legal analysis, investment decisions |
| Pros | Reduced errors, multiple perspectives, built-in verification |
| Cons | Slower execution, 3-4x token cost, may still reach wrong consensus |
| Tools | Custom implementations, LangGraph multi-path with aggregation |
Choosing the Right Pattern
| Use Case | Recommended Pattern | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Content creation pipeline | Hierarchical or Pipeline | Medium |
| Research synthesis | Pipeline + Hierarchical hybrid | High |
| Code review | Specialist Pool or Debate | Medium |
| Customer support | Specialist Pool | Low-Medium |
| Decision support | Debate/Consensus | High |
| Creative brainstorming | Peer-to-Peer | Medium |
| Data processing | Pipeline | Low |
| Complex project management | Hierarchical + specialist sub-agents | High |
💡 Pro Tip: Start with simpler patterns (Pipeline or Hierarchical) and evolve to more complex ones only when needed. Over-engineering multi-agent systems is a common mistake.
Visual Builders: Dify, Flowise, LangFlow
If you prefer visual development:
| Tool | Strength | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Dify (v1.11.2) | RAG engine, LLMOps, prompt IDE | Production AI apps |
| Flowise | LangChain integration, 100+ models | Complex multi-agent |
| LangFlow | Beginner-friendly, free cloud | Rapid prototyping |
I recommend LangFlow for beginners (free cloud service, Desktop app since April 2025), Dify for production deployments, and Flowise for enterprise teams (especially after the Workday acquisition).
Automation Platforms with AI Superpowers
Now let’s look at platforms that connect AI to your actual business tools. These are where AI meets real-world productivity.
Zapier: From IFTTT to AI Orchestration
Zapier has transformed dramatically in 2025 from “if-this-then-that” triggers to a full AI orchestration platform. Key features:
- Zapier Agents (Beta): Autonomous AI teammates that reason and decide, work 24/7, and handle tasks like processing leads, managing support tickets, and research
- Zapier Canvas: Visual process mapping that becomes functioning automation
- AI by Zapier Step: Multi-model support (GPT, Claude, Gemini) for text analysis, categorization, and generation
- Natural Language Setup: Configure agents using plain English instructions
- Live Data Integration: Agents access real-time data from connected apps (HubSpot, Notion, Airtable)
- MCP Integration: 30,000+ actions with minimal setup
With 8,000+ app integrations and ~500 AI-specific apps, it’s the largest ecosystem. Best for non-technical users who need quick wins.
💡 Tip: Unlike rigid Zaps, Zapier Agents use AI to make contextual decisions. They’re ideal for ambiguous tasks that require judgment.
Source: Zapier AI Documentation
n8n 2.0: The Self-Hosted Powerhouse
The stable 2.0 release dropped on December 15, 2025 (n8n Release Notes), with a focus on security, reliability, and production-readiness:
AI Features:
- 70+ AI Nodes: LLMs, embeddings, vector databases, vision, speech
- Agentic Workflows: Agents that plan, execute, and optimize
- AI Workflow Builder: Natural language → workflow generation
- Agent as Tool: Specialized agents as tools for parent agents
- Model Selector Node: Dynamic AI model switching with fallbacks
What’s New in 2.0:
- Secure by Default: Task runners now enabled by default to isolate code execution; environment variables blocked from Code nodes
- Publish/Save Paradigm: New workflow model separates saving edits from publishing to production—no more accidental live updates
- 10x Performance: New SQLite pooling driver delivers massive speed improvements
- Improved UI: Updated canvas and sidebar for better readability
Breaking Changes to Know:
- MySQL/MariaDB support ended—migrate to PostgreSQL
n8n --tunnelcommand removed
The killer advantage: self-hosted = data privacy and control. No per-execution fees—you only pay for API calls to AI providers.
Source: n8n 2.0 Release Blog
Activepieces: Open-Source with Maximum MCP
This MIT-licensed alternative deserves attention:
- 570+ MCP Server Tools: Most extensive MCP support available—highlighted in GitHub Trending (December 2025)
- December 22, 2025 Update: Improved ease of use, speed, and security for MCP integrations
- AI-First Design: Native LLM integration, smart routing based on content analysis
- Copilot Builder: AI-guided workflow creation
- Self-Hostable: Complete data control with TypeScript extensibility
Best for privacy-conscious teams and developers who want open-source.
Source: Activepieces Documentation
Microsoft Copilot Studio + Power Automate
For enterprises in the Microsoft ecosystem:
- GPT-5 Integration (December 2025): GPT-5 Chat now generally available in US and EU; GPT-5.2 available for Microsoft 365 Copilot users
- Agent Flows: AI-first automation backbone optimized for autonomous, conversational AI workflows
- Computer Use (2025 Release Wave 2): Agents interact with websites and desktop apps by mimicking human interaction—even without available APIs
- M365 Integration: Deep Office 365 connectivity with agents available in OneDrive
- MCP Support: Substantial progress in integrating Model Context Protocol across the agent ecosystem
- Agent Builder to Copilot Studio: Seamless transfer of agents from M365 Agent Builder to full Copilot Studio
- Automated Agent Evaluation: Public preview for systematic, scalable agent testing and validation
⚠️ Security Note: Researchers have identified prompt injection risks in Copilot Studio AI agents as of December 2025. The “Connected Agents” feature (enabled by default) can potentially be exploited for backdoor access. Implement strong governance, access controls, and data segmentation.
Source: Microsoft Copilot Studio Documentation, Microsoft Ignite 2025
Platform Quick Comparison
| Platform | Best For | AI Agents | Self-Host | MCP Support | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zapier | Non-technical users | ✅ Beta | ❌ No | ✅ 30K+ actions | $$ SaaS |
| n8n 2.0 | Developers | ✅ Built-in | ✅ Yes | 🔜 Coming | $ Self-host |
| Activepieces | Privacy-focused | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ 570+ tools | Free/Open |
| Copilot Studio | Microsoft enterprises | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Growing | $$$ Enterprise |
Automation Platform Comparison
December 2025 feature comparison
Zapier: 8,000+ integrations, AI Agents, Canvas
Sources: Zapier • n8n • Activepieces
Custom GPTs, Claude Projects & MCP
Let’s talk about creating personalized AI assistants without code.
Custom GPTs: Your No-Code Specialist
Custom GPTs are personalized ChatGPT instances. You can:
- Define custom instructions and personality
- Upload knowledge documents (20 files, 512MB each, 2M tokens per file)
- Enable web browsing, image generation, code interpreter
- Integrate with third-party APIs via custom actions
- Share through the GPT Store
Available to: ChatGPT Plus, Team, Enterprise, and Edu users
Best for: Quick, specific task specialists. I have Custom GPTs for code review, writing style checking, and meeting prep.
Claude Projects: Deep Work Workspaces
Claude Projects are persistent context workspaces. Features include:
- Large knowledge base integration (200K token context)
- Custom system instructions per project
- Maintained context across conversations
- Team collaboration features
- Memory capabilities (Enterprise, Max, Pro): Claude remembers relevant context from past conversations
- Skills as Open Standard (December 2025): Teach Claude repeatable workflows portable across AI platforms
- Incognito chats: Conversations excluded from memory when needed
Available to: Claude Pro, Max, Team, and Enterprise users
Best for: Complex, long-term projects requiring deep analysis. I use Claude Projects for documentation work and research synthesis.
Custom GPTs vs Claude Projects
| Aspect | Custom GPTs | Claude Projects |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Ease | AI-guided, very easy | Manual, moderate |
| Knowledge Base | 20 files, 512MB each | Larger capacity |
| Context Window | 400K (GPT-5.2) | 200K (Claude Opus 4.5) |
| External Actions | ✅ Custom APIs | Limited |
| Memory | Via conversation history | ✅ Cross-conversation memory |
| Best For | Quick specialists | Deep analysis |
| Code Quality | Good | Excellent |
| Collaboration | GPT Store sharing | Team workspaces |
The Model Context Protocol (MCP): December 2025’s Biggest Deal
MCP is an open, vendor-neutral standard for AI-to-tool communication. Think of it as “USB-C for AI”—one protocol, universal connectivity. For a complete introduction, see the MCP Introduction guide.
Before MCP: Each AI vendor had proprietary tool-calling methods. Building an integration for Claude wouldn’t work with ChatGPT. Migrations were painful.
After MCP: A single standard works with any MCP-compatible AI. Build once, use everywhere.
💡 Analogy: Remember when every phone had a different charger? MCP is the USB-C of AI—one connector that works with everything.
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#4f46e5', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#3730a3', 'lineColor': '#6366f1', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart TB
A["AI Application\n(Claude, ChatGPT, etc.)"] <--> B["MCP Protocol Layer"]
B <--> C["MCP Server 1:\nFile System"]
B <--> D["MCP Server 2:\nDatabase"]
B <--> E["MCP Server 3:\nWeb APIs"]
B <--> F["MCP Server N:\nCustom Tools"]The December 2025 MCP Moment
The pace of MCP adoption in December 2025 has been extraordinary:
| Date | Development | Source |
|---|---|---|
| December 9 | Linux Foundation launches AAIF with MCP as foundation | Linux Foundation |
| December 9 | Anthropic transfers MCP ownership to AAIF to ensure neutral governance | Anthropic |
| December 10 | Google announces MCP support for Gemini and Google Cloud | |
| December 2025 | AWS Knowledge MCP Server reaches general availability | AWS |
Current MCP Adoption:
- 10,000+ public MCP servers registered
- Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, Microsoft Copilot all support MCP
- Cursor, Windsurf and other AI IDEs have native MCP integration
- Zapier: 30,000+ actions available via MCP
- Activepieces: 570+ MCP tools
AAIF Founding Projects:
- MCP (Anthropic): The core protocol for AI-tool communication
- Goose (Block): Open-source AI agent framework
- AGENTS.md (OpenAI): Standard for providing AI coding agents with project-specific guidance
This is the inflection point. The major players have aligned on an open standard, preventing vendor lock-in and accelerating innovation.
Sources: Linux Foundation AAIF Announcement, MCP Documentation, Wikipedia MCP
MCP Specification Updates (November 2025)
The MCP specification received a major update on November 25, 2025, introducing critical new capabilities:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Asynchronous Tasks | Experimental “Tasks” primitive for long-running operations that survive disconnections |
| OAuth 2.1 Authorization | Modernized framework with machine-to-machine authentication and enterprise IdP controls |
| Improved Scalability | Better horizontal scaling and streamlined session management for enterprise deployments |
| Formal Extensions | Modular extension system starting with authorization extensions |
| Standardized Tool Names | Improved developer experience with clearer request payload separation |
These updates address key enterprise challenges and make MCP more robust for production deployments.
Source: MCP Specification
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Ecosystem
The "USB-C for AI" — December 2025
Claude
Native
ChatGPT
Integrated
Gemini
Dec 2025
AWS
GA
Cursor
Integrated
Zapier
30K+ actions
Dec 9
AAIF Founded
Dec 10
Google MCP Support
10K+
Active MCP Servers
🔌 Breaking News: The Linux Foundation launched the Agentic AI Foundation (AAIF) on December 9, 2025, with Anthropic's MCP as the foundational contribution. OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and AWS are founding members.
Sources: Linux Foundation AAIF • Google Cloud MCP • Anthropic MCP
Designing Your AI Workflow: The AUDIT Framework
Let me share a practical framework for identifying and implementing AI workflow opportunities.
The AUDIT Framework
- Analyze: Map current workflows and pain points
- Uncover: Identify AI-suitable tasks
- Design: Architect the AI-enhanced workflow
- Implement: Build using appropriate tools
- Track: Measure and optimize performance
Identifying AI Opportunities
Not everything should be automated with AI. Here’s my mental model:
| High AI Potential ✅ | Low AI Potential ❌ |
|---|---|
| Data extraction/summarization | Highly creative original work |
| Email/document drafting | Relationship-critical decisions |
| Research compilation | Legally sensitive approvals |
| Code generation/review | Confidential strategy |
| Content repurposing | Emotional support situations |
| Meeting summaries | Physical tasks |
Building Your Integrated AI Stack
Here’s how I organize tools by category:
Communication Layer:
- Email: Superhuman AI, Gmail AI, Outlook Copilot
- Chat: Slack AI, Teams Copilot
- Meetings: Otter.ai, Fireflies.ai, Zoom AI
Development Layer:
- IDE: Cursor, Windsurf, VS Code + Copilot, Antigravity, Kiro
- CLI: Claude Code, GitHub Copilot CLI, Aider
- Review: CodeRabbit, Sourcery
Content Layer:
- Writing: ChatGPT, Claude, Jasper
- Images: Midjourney, DALL-E 3, Ideogram 3 (see the AI Image Generation guide)
- Video: Sora 2.0, Runway Gen-4.5, Kling 2.6 (see the AI Video Generation guide)
Research Layer:
- Search: Perplexity Pro, Google AI Overviews, Gemini Deep Research
- Documents: NotebookLM, Elicit, Consensus
Sample Workflow: The “Zero Inbox” System
Here’s a concrete example I use daily:
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#4f46e5', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#3730a3', 'lineColor': '#6366f1', 'fontSize': '16px' }}}%%
flowchart LR
A["📧 Email\nArrives"] --> B["🤖 AI\nClassifier"]
B --> C{"Priority?"}
C -->|Urgent| D["⚡ Slack Alert\n+ Draft Reply"]
C -->|Normal| E["📋 Daily Digest\n+ Suggestions"]
C -->|Newsletter| F["📝 Summarize\n+ Archive"]
C -->|Spam| G["🗑️ Delete\n+ Update Filter"]
D --> H["✅ Done"]
E --> H
F --> H
G --> H- Email arrives → Zapier/n8n trigger
- AI classifies into urgent/normal/spam/newsletter
- Urgent: Immediate Slack notification + draft response
- Normal: Daily digest at 9 AM with suggested replies
- Newsletter: Auto-summarize key points + archive
- Spam: Auto-delete + update filter rules
This takes 10 minutes to set up and saves me 30+ minutes daily.
AI Workflows for Specific Industries
Different industries have unique workflow needs, compliance requirements, and integration patterns. Here’s how to apply agentic AI in your sector.
Healthcare & Life Sciences
Healthcare workflows require extra attention to privacy (HIPAA, GDPR) and accuracy (patient safety).
High-Value Workflow Opportunities:
| Workflow | Description | Estimated Time Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Communication | Appointment reminders, follow-up surveys, symptom triage | 2-3 hours/day per coordinator |
| Clinical Documentation | AI-assisted note-taking, coding suggestions, compliance checks | 30-45 min per physician/day |
| Prior Authorization | Automatic form completion, status tracking, appeals drafting | 4-6 hours/day per staff member |
| Literature Monitoring | Drug safety signals, clinical trial updates, guideline changes | 90% faster than manual review |
Sample Workflow: Patient Intake Automation
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#10b981', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff' }}}%%
flowchart LR
A[Patient Form] --> B[Extract Data]
B --> C[Validate Info]
C --> D[Risk Assessment]
D --> E[Provider Matching]
E --> F[Schedule + Confirm]⚠️ HIPAA Considerations: Use BAA-compliant AI providers (OpenAI Enterprise, Anthropic, Google Cloud Healthcare API). Never include PHI in prompts sent to consumer-tier APIs. Implement audit logging for all AI-assisted decisions.
Financial Services
Finance workflows benefit from AI’s ability to process structured data and detect patterns.
High-Value Workflow Opportunities:
| Workflow | Description | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fraud Detection | Real-time transaction analysis, anomaly flagging | Reduce fraud losses 40-60% |
| KYC/Onboarding | Document verification, risk assessment, watchlist screening | 70% faster onboarding |
| Investment Research | News monitoring, sentiment analysis, report generation | 10x more coverage |
| Regulatory Reporting | Automated filing, audit trail, compliance checks | 90% time reduction |
Sample Workflow: Loan Application Processing
- Document Ingestion → Extract data from pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements
- Data Validation → Cross-reference against application, flag discrepancies
- Risk Scoring → Calculate creditworthiness using approved models
- Decision Routing → Auto-approve/decline within policy, escalate edge cases
- Documentation → Generate approval letters, disclosure documents
💡 Compliance Tip: Maintain human-in-the-loop for final credit decisions to comply with ECOA and fair lending requirements. Log all AI recommendations with explanations for audit purposes.
Legal
Legal workflows combine document-heavy processing with high accuracy requirements.
High-Value Workflow Opportunities:
| Workflow | Description | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Contract Review | Clause extraction, risk identification, redlining suggestions | 60-80% faster review |
| Legal Research | Case law search, precedent analysis, brief drafting | 5x research productivity |
| Due Diligence | Document classification, entity extraction, timeline construction | 70% cost reduction |
| E-Discovery | Document review, privilege analysis, production automation | 50-90% cost savings |
Sample Workflow: Contract Analysis Pipeline
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#8b5cf6', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff' }}}%%
flowchart TD
A[Contract Upload] --> B[OCR + Parse]
B --> C[Clause Extraction]
C --> D[Risk Scoring]
D --> E[Comparison to Standard]
E --> F[Summary + Redlines]
F --> G[Attorney Review Queue]⚠️ Ethics Note: AI-generated legal analysis should always be reviewed by licensed attorneys. Maintain attorney-client privilege by using enterprise deployments and secure data handling.
Marketing & Sales
Marketing and sales workflows focus on personalization, speed, and scale.
High-Value Workflow Opportunities:
| Workflow | Description | Metric Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Qualification | Scoring, enrichment, intelligent routing | 3x more qualified leads |
| Content Production | Topic research, drafting, multi-format repurposing | 5-10x content output |
| Campaign Optimization | A/B analysis, performance prediction, budget reallocation | 20-40% improved ROAS |
| Competitive Intelligence | Monitoring, analysis, automated alerts | Real-time awareness |
Sample Workflow: Inbound Lead Processing
- Lead Capture → Form submission triggers workflow
- Data Enrichment → Append company info, social profiles, tech stack
- Intent Scoring → Analyze behavior patterns, content engagement
- Segmentation → Route to appropriate sequence based on score + persona
- Personalization → Generate customized outreach using lead data
- CRM Update → Create/update records with full context
💡 Personalization at Scale: Use AI to generate email variations, but maintain brand voice through Custom GPTs with style guides uploaded as knowledge.
Manufacturing & Supply Chain
Manufacturing workflows benefit from AI’s pattern recognition and prediction capabilities.
High-Value Workflow Opportunities:
| Workflow | Description | Operational Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Demand Forecasting | Historical analysis, trend detection, inventory optimization | 20-30% inventory reduction |
| Quality Control | Defect detection, root cause analysis, corrective actions | 50% fewer defects shipped |
| Predictive Maintenance | Equipment monitoring, failure prediction, work orders | 25-40% less downtime |
| Supplier Management | Performance monitoring, risk assessment, communication | 15% cost savings |
Sample Workflow: Quality Incident Response
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#f59e0b', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff' }}}%%
flowchart LR
A[Defect Detected] --> B[Classify Issue]
B --> C[Root Cause Analysis]
C --> D[Generate CAPA]
D --> E[Assign + Track]
E --> F[Verify + Close]Education
Education workflows focus on personalization and administrative efficiency.
High-Value Workflow Opportunities:
| Workflow | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Student Support | 24/7 Q&A, resource recommendations, progress tracking | 60% faster response time |
| Content Creation | Lesson plans, assessments, feedback generation | 3-5 hours saved per week |
| Administrative Automation | Enrollment, scheduling, communications | 40% admin time reduction |
| Accessibility | Auto-captioning, translation, content adaptation | Improved inclusivity |
Sample Workflow: Assignment Feedback
- Submission Received → Student uploads assignment
- Plagiarism Check → Automated originality verification
- AI Pre-Review → Generate rubric-based feedback draft
- Instructor Review → Faculty reviews, edits, approves
- Delivery → Personalized feedback sent with improvement suggestions
⚠️ Academic Integrity: Clearly disclose AI use in feedback. Use AI as a first-pass reviewer, not a replacement for instructor judgment.
Measuring Success: ROI and Productivity Metrics
Let’s talk numbers. December 2025 research across multiple sources paints a compelling picture of AI workflow ROI.
The Productivity Reality
Time Savings (December 2025):
| Role Category | Daily Time Saved | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Average enterprise user | 40-60 minutes | OpenAI Enterprise Report |
| Heavy AI users | 10+ hours weekly | OpenAI Enterprise Report |
| Data Scientists & Engineers | 60-80 minutes | OpenAI Enterprise Report |
| Professional service workers | 200 hours annually | Raven Labs 2025 |
💡 Key Insight: Companies that embed change management from the start see double the adoption rates compared to those that don’t. (Superhuman Enterprise Study)
Output Improvements:
- 75% of workers report AI improved speed OR quality of output (OpenAI 2025)
- 66% average performance improvement with generative AI (McKinsey GenAI Research)
- 40% faster work overall for companies using AI-powered solutions (CFlowApps 2025)
- 27% reduction in data entry errors for AI-assisted employees (McKinsey 2025)
- 13.8% more customer inquiries handled per hour (Stanford HAI Research)
Daily Time Savings by Role
Minutes saved per day with AI workflows (Dec 2025)
🚀 Key Insight: Heavy AI users save 10+ hours weekly. Data science and engineering roles see the highest productivity gains.
Sources: OpenAI Enterprise Report • EY AI Survey 2025
Calculating Your AI Workflow ROI
| Metric | What to Measure | Target | How to Track |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time Saved | Hours saved × Hourly rate | Track weekly | Time tracking tools |
| Quality Improvement | Error reduction × Cost per error | Monthly audit | Before/after comparison |
| Throughput Gain | New output / Previous output | Per workflow | Project metrics |
| Tool Cost | Subscription + API usage | Monthly budget | Billing dashboards |
| Net ROI | (Value generated - Costs) / Costs × 100 | >100% | Quarterly review |
Enterprise Benchmarks (December 2025)
Research from leading firms shows strong ROI patterns:
| Metric | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
| AI deployments achieving ROI in Year 1 | 74% | Google AI Research |
| Time to full ROI | 5-6 months | Nitro Document AI Study |
| Average Year 1 return | 2.5x investment | Nitro Document AI Study |
| Annual productivity value per 1,000 employees (document AI) | $26 million | Nitro Document AI Study |
| Executives reporting measurable financial improvement | 56% | Deloitte AI Survey 2025 |
| Organizations achieving >5% cost reduction from AI | 15% | McKinsey State of AI 2025 |
Typical AI Workflow ROI Timeline
74% of deployments achieve ROI within Year 1
Setup & Learning
First Workflows Live
Full ROI Achieved
2.5x Return
5-6 mo
Average time to full ROI
$26M
Annual value per 1,000 employees
Sources: Google Research • Nitro Document AI
Where Companies Reinvest AI Gains
Instead of just cutting headcount, smart companies are reinvesting productivity gains:
| Investment Area | % of Companies | Strategic Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Expanding existing AI capabilities | 47% | Deepening competitive moats |
| Developing new AI capabilities | 42% | Creating new value streams |
| Strengthening cybersecurity | 41% | Protecting AI systems |
| R&D investment | 39% | Future innovation |
| Employee upskilling | 38% | Human-AI collaboration |
Source: McKinsey State of AI 2025
🎯 Reality Check: While the productivity potential is enormous, only 15% of organizations are achieving significant cost reductions from AI. The difference? Change management, clear use cases, and measuring what matters.
AI Workflow ROI Calculator
Estimate your potential savings
Weekly Value
$600
Monthly Value
$2,400
Annual Value
$28,800
Based on average time savings reported by enterprise AI users (OpenAI Enterprise Report, December 2025)
Cost Management and Optimization
Let’s be practical about costs. Understanding the full cost picture helps you budget effectively and optimize spending.
Understanding AI Workflow Costs
| Cost Category | Examples | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Model API calls | GPT-5.2, Claude API | Caching, smaller models for simple tasks |
| Platform subscriptions | Zapier, n8n Cloud | Annual plans, usage-based tiers |
| Custom development | Agent frameworks | Open-source alternatives |
| Maintenance | Updates, monitoring | Automated testing, observability |
| Compute/hosting | Self-hosted infrastructure | Right-size servers, use spot instances |
Complete Platform Pricing (December 2025)
| Platform | Free Tier | Starter | Professional | Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zapier | 100 tasks/mo | $29.99/mo (750 tasks) | $73.50/mo (2K tasks) | Custom |
| n8n Cloud | — | $24/mo (2.5K executions) | $60/mo (10K executions) | Custom |
| n8n Self-Host | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Support-only pricing |
| Activepieces | 1K tasks/mo | $10/mo (10K tasks) | $50/mo (100K tasks) | Custom |
| Make | 1K ops/mo | $10.59/mo (10K ops) | $18.82/mo (10K ops) | Custom |
| Copilot Studio | — | Included with M365 | $30/user/mo | Custom |
Detailed Model API Costs (December 2025)
| Model | Provider | Input $/1M | Output $/1M | Context | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o mini | OpenAI | $0.15 | $0.60 | 128K | Classification, simple tasks |
| GPT-4o | OpenAI | $2.50 | $10.00 | 128K | General purpose |
| GPT-5.2 | OpenAI | $5.00 | $15.00 | 400K | Complex agentic tasks |
| o3 | OpenAI | $15.00 | $60.00 | 200K | Advanced reasoning |
| Claude Haiku 4.5 | Anthropic | $0.80 | $4.00 | 200K | Fast, cost-effective |
| Claude Sonnet 4.5 | Anthropic | $3.00 | $15.00 | 200K | Balanced performance |
| Claude Opus 4.5 | Anthropic | $15.00 | $75.00 | 200K | Maximum capability |
| Gemini 3 Flash | $0.075 | $0.30 | 1M | Speed-optimized | |
| Gemini 3 Pro | $1.25 | $5.00 | 1M | Multimodal, long context | |
| LLaMA 4 (self-hosted) | Meta | $0 (compute only) | $0 | 10M | Privacy, cost control |
The Model Selection Matrix
Match task complexity to model capability (and cost):
| Task Complexity | Recommended Model | Cost/1M Tokens (Dec 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Simple classification | GPT-4o mini, Haiku | $0.15 - $0.75 |
| Standard generation | GPT-4o, Sonnet 4.5 | $2.50 - $15.00 |
| Complex reasoning | o3, Opus 4.5 | $15.00 - $60.00 |
| Maximum capability | o3-Pro, GPT-5.2 Pro | $60.00+ |
Monthly Cost Scenarios
Realistic cost estimates based on common use cases:
| Workflow Type | Daily Runs | Tokens/Run | Model | Est. Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple email triage | 100 | 2K in / 500 out | GPT-4o mini | ~$12 |
| Research assistant | 20 | 10K in / 5K out | Claude Sonnet | ~$45 |
| Document analyzer | 50 | 20K in / 3K out | GPT-4o | ~$90 |
| Sales lead processor | 200 | 5K in / 2K out | GPT-4o | ~$120 |
| Content production | 10 | 15K in / 10K out | Claude Opus | ~$350 |
| Multi-agent research | 30 | 50K in / 20K out | Mixed | ~$250-500 |
Cost Optimization Strategies
1. Tiered Model Routing
Input → Classifier (GPT-4o mini) →
→ Simple task → GPT-4o mini
→ Medium task → GPT-4o
→ Complex task → Opus 4.5Savings: 50-70% vs. using premium model for everything
2. Response Caching
- Cache identical or similar queries
- Use semantic similarity for cache hits
- Set appropriate TTL (time-to-live)
- Potential savings: 20-40%
3. Prompt Optimization
- Reduce verbose instructions
- Use concise examples
- Compress context where possible
- Savings: 10-25% per request
4. Batch Processing
- Group similar requests
- Process during off-peak hours
- Reduce per-request overhead
- Savings: 15-30%
Smart Routing Strategies
- Use smaller models for initial classification, then route complex queries to capable models
- Cache frequent responses to avoid repeated API calls
- Implement fallback chains: try expensive model first with timeout, fall back to cheaper if needed
- Set hard limits on API spend with alerts
- Monitor cost per outcome, not just cost per call
The n8n Advantage: Self-Hosting Economics
If you’re cost-sensitive and technical:
- No per-execution fees
- Only pay for API calls to AI providers
- Control over data residency
- Higher initial setup, lower long-term cost
Break-even analysis:
| Scenario | n8n Cloud | n8n Self-Host (AWS) |
|---|---|---|
| 5K executions/mo | $24/mo | ~$20/mo (t3.small) |
| 50K executions/mo | $120/mo | ~$40/mo (t3.medium) |
| 500K executions/mo | $600+/mo | ~$100/mo (t3.large) |
Self-hosting wins at scale, especially for high-volume workflows.
Best Practices for Production Agentic Systems
When you’re ready to go to production, these principles matter.
Reliability Patterns
- Timeouts and Retries: Don’t let agents run forever
- Fallback Models: If primary fails, use backup
- Human-in-the-Loop: Critical decisions require approval
- Idempotency: Same request twice = same result
- State Persistence: Survive crashes and restarts
Security Considerations
Agentic systems introduce unique security challenges. Address these comprehensively:
Core Security Practices:
- Never expose API keys in agent prompts or logs
- Validate all external data before processing
- Implement rate limiting on agent actions
- Audit log all agent decisions and actions
- Use sandboxed environments for code execution (n8n 2.0 does this by default)
Prompt Injection Prevention:
| Attack Type | Description | Defense |
|---|---|---|
| Direct injection | Malicious instructions in user input | Input sanitization, instruction hierarchy |
| Indirect injection | Malicious content in external data sources | Data validation, content scanning |
| Jailbreaking | Attempts to bypass safety guidelines | Strong system prompts, output filters |
| Data exfiltration | Tricking agent to send data externally | Output monitoring, URL allowlists |
Defense Strategies:
## Prompt Defense Patterns
1. **Clear instruction hierarchy**:
"SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS (never override): [rules]
USER REQUEST (may be untrusted): [input]"
2. **Input sanitization**:
- Remove or escape special characters
- Truncate excessively long inputs
- Validate against expected format
3. **Output validation**:
- Check for sensitive data before sending
- Verify outputs match expected schema
- Scan for forbidden content/URLsSecrets Management:
- Store API keys in secure vaults (AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault)
- Rotate credentials regularly
- Use least-privilege access for each workflow
- Never log secrets, even accidentally
- Use environment variables, not hardcoded values
Data Sanitization Checklist:
- Strip PII from prompts before sending to AI
- Mask sensitive data in logs
- Validate file types before processing
- Scan attachments for malware
- Implement data retention policies
Observability Requirements
| Aspect | What to Track | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Logging | Every agent decision and tool call | Custom, LangSmith |
| Tracing | End-to-end request flow | LangSmith, Helicone |
| Metrics | Latency, success rate, cost per workflow | Prometheus, custom |
| Alerting | Failures, budget overruns, anomalies | PagerDuty, Slack |
Setting Up LangSmith for Observability:
- Install:
pip install langsmith - Set environment variables:
LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2=true,LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=your_key - All LangChain operations automatically traced
- View in LangSmith dashboard: latency, tokens, errors per run
Cost Tracking Dashboard:
- Track cost per workflow type
- Alert on unusual spend patterns
- Set daily/weekly budget limits
- Compare cost vs. value delivered
Testing Agentic Workflows
- Unit tests for individual agent components
- Integration tests for tool interactions
- End-to-end tests for complete workflows
- Evaluation sets for quality assessment
- A/B testing for prompt variations
Governance and Compliance
- Document all AI decision-making processes
- Maintain human oversight for high-stakes actions
- Regular bias and fairness audits
- Compliance with industry regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.)
- Clear escalation paths for agent failures
Enterprise Deployment & Scaling
When deploying AI workflows at enterprise scale, additional considerations come into play.
Architecture Patterns for Scale
1. Multi-Tenant Architecture
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#4f46e5', 'primaryTextColor': '#ffffff' }}}%%
flowchart TD
A[API Gateway] --> B[Tenant Router]
B --> C1[Tenant A Workflows]
B --> C2[Tenant B Workflows]
B --> C3[Tenant C Workflows]
C1 --> D[Shared AI Services]
C2 --> D
C3 --> D
D --> E[(Tenant-Isolated Data)]Key Requirements:
- Tenant isolation at data and execution levels
- Per-tenant usage tracking and billing
- Shared infrastructure for cost efficiency
- Configurable per-tenant limits
2. High-Availability Setup
| Component | Primary | Failover | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| API Gateway | AWS ALB Region 1 | AWS ALB Region 2 | Automatic |
| Workflow Engine | n8n Primary | n8n Replica | Under 30 seconds |
| Database | PostgreSQL Primary | PostgreSQL Replica | Under 60 seconds |
| Queue | Redis Primary | Redis Sentinel | Under 30 seconds |
Scaling Strategies
Horizontal Scaling:
- Run multiple n8n workers behind a load balancer
- Stateless workflow execution where possible
- Use Redis for shared state and queuing
- Scale based on queue depth, not just CPU
Vertical Scaling Limits:
- Single n8n instance: ~500-1000 concurrent executions
- Beyond this: must scale horizontally
- Database often becomes bottleneck first
Auto-Scaling Configuration (Kubernetes):
# HPA configuration for n8n workers
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: n8n-worker-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: n8n-worker
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 60Disaster Recovery
Backup Strategy:
| Data Type | Backup Frequency | Retention | Recovery Point Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workflow definitions | Every change + daily | 90 days | Last successful version |
| Execution history | Daily | 30 days | Previous day |
| Credentials | Encrypted, every change | Indefinite | Last known good |
| Configuration | Git-versioned | Indefinite | Any previous version |
Recovery Procedures:
- Workflow corruption: Restore from Git or last known good backup
- Database failure: Failover to replica, restore from backup if needed
- Total site failure: Spin up in secondary region, restore from backups
- Credential compromise: Rotate all secrets, re-deploy with new values
Compliance Considerations
| Regulation | Key Requirements | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Data residency, right to deletion | EU-only processing, deletion workflows |
| HIPAA | PHI protection, audit trails | BAA with vendors, encryption, logging |
| SOC 2 | Security controls, monitoring | Access controls, incident response |
| PCI-DSS | Cardholder data protection | Tokenization, network segmentation |
Compliance Checklist:
- Data processing agreements with all AI providers
- Data residency requirements documented and enforced
- Audit logging enabled for all AI decisions
- Regular security assessments conducted
- Incident response plan includes AI-specific scenarios
- Employee training on AI governance completed
Team & Role Structure
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| AI Platform Owner | Strategy, vendor selection, governance |
| Workflow Developer | Building and maintaining workflows |
| AI Operations | Monitoring, scaling, incident response |
| Security/Compliance | Reviews, audits, policy enforcement |
| Business Stakeholder | Requirements, acceptance, ROI tracking |
Troubleshooting Common Workflow Problems
When workflows fail, quick diagnosis is critical. Here’s a comprehensive troubleshooting guide.
Agent Behavior Issues
| Problem | Symptoms | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agent loops infinitely | Never completes, burns tokens rapidly | Missing stop condition or exit criteria | Add max iterations, timeout limits, explicit stop conditions |
| Agent ignores instructions | Wrong outputs, doesn’t follow format | Poor prompt structure, buried instructions | Move critical instructions to top, use headers, add examples |
| Agent uses wrong tools | Calls irrelevant APIs, errors | Tool descriptions unclear or overlapping | Improve tool descriptions, add usage examples, clarify when to use each |
| Agent stops prematurely | Incomplete results, truncated output | Context window exceeded or max tokens hit | Implement chunking, summarization, or increase limits |
| Agent hallucinates data | Made-up facts, non-existent URLs | No grounding, insufficient constraints | Add “only use provided tools” constraint, require source citations |
| Inconsistent outputs | Different results for same input | Temperature too high, vague instructions | Lower temperature (0.1-0.3), add format examples |
Integration and API Failures
| Problem | Symptoms | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| API timeouts | Workflow hangs, partial completion | Slow external service, network issues | Increase timeouts (30-60s), add retries, implement async |
| Authentication failures | 401/403 errors | Expired tokens, wrong scopes | Implement token refresh, verify permissions, check API key |
| Rate limiting | 429 errors, throttling messages | Too many requests in short period | Add delays between calls, implement request queuing, use backoff |
| Data format mismatches | Parse errors, type errors | Schema changes, unexpected nulls | Add validation layer, handle edge cases, version your schemas |
| Webhook failures | Missing triggers, silent failures | Endpoint down, payload issues | Add health checks, implement dead letter queues, log all payloads |
Performance Problems
| Problem | Symptoms | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow execution | Minutes for simple tasks | Over-engineered workflow, serial execution | Simplify, parallelize independent steps, use faster models |
| High costs | Budget exceeded, unexpected bills | Wrong model selection, token waste | Use tiered routing, cache responses, optimize prompts |
| Memory issues | State lost, crashes | Large context accumulation | Implement summarization, clean up intermediate state |
| Inconsistent latency | Some runs fast, some slow | Cold starts, variable API response | Pre-warm connections, add timeout fallbacks |
Common Error Messages and Fixes
“Maximum context length exceeded”
Error: This model's maximum context length is 128000 tokens- Cause: Input + expected output exceeds model limits
- Fix: Implement chunking, use summarization for long contexts, or switch to larger context model
“Tool not found” or “Function not defined”
Error: Tool 'web_search' is not available- Cause: MCP server not running, tool not registered
- Fix: Verify server status, check tool registration, confirm tool name matches exactly
“Rate limit exceeded”
Error: Rate limit reached for requests. Retry after 60 seconds.- Cause: Too many API calls in short period
- Fix: Implement exponential backoff, add request queuing, consider upgrading tier
“Invalid JSON response”
Error: Expected valid JSON but received malformed response- Cause: Model didn’t follow format instructions
- Fix: Use structured output mode, add JSON examples, implement retry with clearer instructions
Debugging Checklist
When a workflow fails, work through this checklist:
- Check logs: What was the last successful step?
- Verify inputs: Are all required inputs present and valid?
- Test connections: Are all external services reachable?
- Review prompts: Did instructions change recently?
- Check limits: Are you within rate limits and quotas?
- Isolate the step: Can you reproduce the failure in isolation?
- Compare to working version: What changed since it last worked?
Workflow Evaluation Framework
How do you know if your workflow is actually working well? Here’s a systematic approach to quality assessment.
The FACTS Framework
Evaluate every workflow against five dimensions:
| Dimension | Question | Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Does it complete the intended task? | Task completion rate |
| Accuracy | Are the outputs correct and reliable? | Error rate, accuracy score |
| Consistency | Does it produce similar results for similar inputs? | Variance across runs |
| Timeliness | Does it complete within acceptable time? | P50/P95 latency |
| Safety | Does it avoid harmful or inappropriate outputs? | Safety incident rate |
Key Metrics to Track
| Metric | Description | Target | How to Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task Completion Rate | % of workflows completing successfully | Above 95% | Count completed / total initiated |
| Output Accuracy | % of outputs that are factually correct | Above 90% | Human evaluation sample, automated checks |
| Latency (P50) | Median time to complete | Under 30s | Track execution times |
| Latency (P95) | 95th percentile completion time | Under 120s | Track execution times |
| Cost per Execution | Total API + platform cost per run | Varies | Sum all costs, divide by runs |
| Error Rate | % of executions with errors | Under 5% | Count errors / total runs |
| Token Efficiency | Output quality per token spent | Improve over time | Quality score / tokens used |
| User Satisfaction | End-user rating of results | Above 4.0/5.0 | Feedback collection |
Building Evaluation Sets
Create structured test sets for systematic quality assessment:
1. Golden Dataset
- Curated inputs with known correct outputs
- Cover common use cases
- Include typical variations
- Update as requirements change
2. Edge Cases
- Unusual inputs that test boundaries
- Empty inputs, very long inputs
- Special characters, multiple languages
- Ambiguous requests
3. Adversarial Inputs
- Deliberately challenging or malformed inputs
- Prompt injection attempts
- Conflicting instructions
- Out-of-scope requests
4. Regression Tests
- Previous failure cases that have been fixed
- Ensure fixes don’t break other functionality
- Add every production bug to this set
Evaluation Scoring Rubric
For human evaluation, use a consistent rubric:
| Score | Label | Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Excellent | Perfect output, no improvements needed |
| 4 | Good | Minor issues, acceptable for use |
| 3 | Acceptable | Some issues, may need light editing |
| 2 | Poor | Significant issues, requires major revision |
| 1 | Fail | Wrong output, factual errors, or harmful content |
Continuous Monitoring Dashboard
Track these metrics in real-time to catch issues early:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ WORKFLOW HEALTH DASHBOARD │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Success Rate: 97.2% ████████████████░░░ │
│ Avg Latency: 12.3s ███████░░░░░░░░░░░░ │
│ Cost Today: $47.82 │
│ Active Runs: 23 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ALERTS │
│ ⚠️ Error rate spike: 8% (threshold: 5%) - 10 min ago │
│ ℹ️ New model version available │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘A/B Testing Workflows
Test variations systematically:
| Element to Test | Method | Success Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Prompt variations | Split traffic 50/50 | Accuracy, user satisfaction |
| Model selection | Parallel execution, compare | Quality-cost tradeoff |
| Tool ordering | Sequential testing | Latency, success rate |
| Temperature settings | Parameter sweep | Output diversity vs consistency |
| Chunking strategies | A/B on document processing | Accuracy on long docs |
💡 Pro Tip: Always run A/B tests for at least 100 executions per variant before drawing conclusions. Small sample sizes lead to misleading results.
Prompt Engineering for Agentic Workflows
The quality of your agent prompts directly determines workflow success. Here’s how to engineer prompts that work reliably at scale.
Agent System Prompt Structure
A well-structured agent prompt has five essential components:
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Identity & Role | Define who the agent is | ”You are a senior financial analyst…” |
| Capabilities | List available tools and actions | ”You can search the web, read files, and create reports” |
| Constraints | Define boundaries and limitations | ”Never make up data. Always cite sources.” |
| Output Format | Specify expected response structure | ”Return results as JSON with schema…” |
| Examples | Demonstrate expected behavior | ”Example: When asked about [X], respond with [Y]“ |
Template: Research Agent
You are a research analyst specializing in {{domain}}.
## Your Capabilities
You have access to the following tools:
- `web_search(query)`: Search the web for current information
- `read_document(url)`: Read and extract content from documents
- `save_finding(title, content, source)`: Store important discoveries
## Constraints
- Only use information from your tools; do not make up facts
- Always cite sources with URLs
- Stop after finding 5 relevant, high-quality sources
- If you cannot find reliable information, say so
## Output Format
Provide your findings as:
1. **Executive Summary** (2-3 sentences)
2. **Key Findings** (bullet list with citations)
3. **Sources** (numbered list with URLs)
4. **Confidence Level** (High/Medium/Low with explanation)
## Example Interaction
User: "Research the latest developments in quantum computing."
You: [Use web_search to find recent articles] → [Read top 3 results] →
[Synthesize findings] → [Format as specified above]Template: Task Execution Agent
You are a workflow automation agent that executes business tasks precisely.
## Available Actions
{{list_of_tools_with_descriptions}}
## Execution Rules
1. **Plan First**: Before acting, state your plan in <thinking> tags
2. **One Step at a Time**: Execute actions sequentially, verify each result
3. **Handle Errors**: If an action fails, try an alternative approach
4. **Confirm Completion**: Summarize what was accomplished
## Safety Constraints
- Never delete data without explicit confirmation
- Never share sensitive information externally
- Always log actions for audit purposes
- Escalate to human if confidence is below 80%
## Response Format
<thinking>
[Your reasoning about how to approach the task]
</thinking>
<action>
[Tool call or action to execute]
</action>
<result>
[Outcome of the action]
</result>Chain-of-Thought for Complex Tasks
Force explicit reasoning before action to improve accuracy:
## Thinking Protocol
Before taking ANY action, you must complete these steps:
1. **UNDERSTAND**: Restate the request in your own words
- What is the user actually asking for?
- What would success look like?
2. **PLAN**: Outline your approach
- What steps are needed?
- What tools will you use?
- What could go wrong?
3. **VALIDATE**: Check your plan
- Does this achieve the goal?
- Is this the most efficient approach?
- Are there any risks?
4. **EXECUTE**: Take action one step at a time
- Complete each step fully before moving on
- Verify results match expectations
5. **VERIFY**: Confirm the outcome
- Did you achieve the goal?
- Is the output correct and complete?Multi-Agent Coordination Prompts
Manager Agent Prompt:
You are a project manager coordinating a team of specialist agents.
## Your Team
- **ResearchAgent**: Gathers and synthesizes information
- **AnalysisAgent**: Processes data and generates insights
- **WriterAgent**: Creates polished, formatted content
- **ReviewerAgent**: Quality checks and provides feedback
## Coordination Protocol
1. Receive user request
2. Decompose into subtasks
3. Assign each subtask to appropriate team member
4. Collect results and handle dependencies
5. Synthesize final output
6. Perform quality check before delivery
## Communication Format
To delegate: `@AgentName: [clear task description with context]`
To collect: Wait for agent response, then proceed to next step
## When to Escalate to Human
- Conflicting results from team members
- Uncertainty about user intent
- Results that could have significant impactPrompt Patterns for Reliability
| Pattern | Use Case | Template |
|---|---|---|
| Structured Output | Need consistent format | ”Respond ONLY in valid JSON matching this schema: [your_schema]“ |
| Constraint-First | Preventing errors | ”CRITICAL RULES (never violate): 1… 2… 3… Now, your task is:“ |
| Step-by-Step | Complex procedures | ”Complete these steps IN ORDER: Step 1… Step 2… Step 3…” |
| Self-Verification | High accuracy needs | ”After completing the task, verify your response by checking: 1… 2…” |
| Fallback Handling | Edge cases | ”If you cannot complete the task, respond with: [error_format]“ |
| Confidence Scoring | Decision support | ”Rate your confidence (1-10) and explain any uncertainties” |
Common Prompt Mistakes and Fixes
| Mistake | Problem | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Vague instructions | Inconsistent outputs | Be specific about format, length, style |
| No examples | Agent guesses behavior | Include 1-3 concrete examples |
| Missing constraints | Hallucinations, errors | Explicitly state what NOT to do |
| No error handling | Workflow breaks | Define fallback behavior |
| Overloaded prompts | Confused agent | Split into multiple specialized agents |
💡 Pro Tip: Test your prompts with edge cases before deploying. The best prompts are refined through iteration—track failures and update accordingly.
Hands-On Tutorial: Build Your First Agentic Workflow
Let’s build something real. We’ll create an Automated Research Assistant that:
- Takes a research topic
- Gathers sources
- Summarizes findings
- Delivers a formatted report
Time required: 30 minutes
Tools: n8n (or Zapier) + Claude API
Step-by-Step Guide
| Step | Action | Tool |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Set up trigger (webhook, email, or form) | n8n/Zapier |
| 2 | Extract research topic from input | AI Text Parser |
| 3 | Search for sources | Perplexity API or web search |
| 4 | Summarize findings | Claude API |
| 5 | Format report | AI Formatter |
| 6 | Deliver output (email, Slack, Notion) | Integration node |
| 7 | Log for analytics | Database/spreadsheet |
Sample Prompt Template
You are a research assistant. Your task is to:
1. **Analyze** the research topic: {{topic}}
2. **Synthesize** information from these sources: {{sources}}
3. **Create** a concise summary (300-500 words)
4. **Include** 3 key insights and 2 action items
5. **List** sources with links
**Format**: Use headers, bullet points, and bold for emphasis.Extending the Workflow
Once the basics work, add:
- Competitor analysis agent
- Trend detection over time
- Automatic scheduling of follow-up research
- Multi-format output (PDF, slides, audio summary)
Error Handling
Add these safeguards to make your workflow production-ready:
## Error Handling Configuration
1. **API Failures**: Retry up to 3 times with exponential backoff
2. **Empty Results**: If no sources found, notify user and suggest refined query
3. **Timeout**: If search takes >30 seconds, use cached results or abort gracefully
4. **Rate Limits**: Queue requests, process with delays
5. **Output Validation**: Verify all required fields present before deliveringTesting Your Workflow
Before going live:
| Test Type | What to Check | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Happy path | Normal request flows through | Complete report delivered |
| Empty input | Blank or minimal topic | Helpful error message |
| Long input | Very detailed topic | Graceful handling, no truncation |
| Invalid topic | Nonsense or harmful request | Safe refusal, no output |
| API failure | Simulate external API down | Retry, then graceful degradation |
Try This Now
Based on your experience level:
| Level | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Beginner | Create a Custom GPT for your specific job function |
| Intermediate | Build a 3-step n8n workflow with AI processing |
| Advanced | Deploy a CrewAI multi-agent team locally |
Workflow Templates Library
Here are ready-to-use templates for common business workflows. Adapt these to your specific needs.
Template 1: Email Auto-Responder
Use Case: Automatically draft responses to incoming emails based on type and urgency.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | New email in inbox |
| Classifier | GPT-4o mini (categorize: urgent/normal/FYI/spam) |
| Draft Generator | Claude Sonnet (tone-appropriate response) |
| Output | Draft saved to drafts folder, notification to user |
Key Prompt: “Based on this email’s content and sender, draft a professional response that addresses their main points. Match their formality level.”
Template 2: Meeting Notes Processor
Use Case: Transform meeting transcripts into actionable summaries.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | Meeting recording completed |
| Transcription | Whisper API or meeting platform export |
| Processor | Claude Opus (extract decisions, action items, key points) |
| Output | Formatted notes to Notion/Confluence + Slack summary |
Key Prompt: “Extract: 1) Key decisions made, 2) Action items with assignees and deadlines, 3) Discussion points requiring follow-up, 4) Topics deferred to next meeting.”
Template 3: Content Repurposing Pipeline
Use Case: Transform one piece of content into multiple formats.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | New blog post published |
| Analyzer | Extract key points, quotes, statistics |
| Generators | Multiple parallel: Twitter thread, LinkedIn post, email newsletter, video script |
| Output | Drafts queued in respective platforms |
Key Prompt: “Transform this blog post into [format]. Maintain the core message but adapt tone and length for [platform] audience.”
Template 4: Customer Support Triage
Use Case: Categorize and route support tickets with AI-suggested responses.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | New support ticket created |
| Classifier | Categorize by type, urgency, sentiment |
| Knowledge Search | RAG against help docs |
| Response Generator | Draft response using relevant docs |
| Router | Assign to appropriate team queue |
Key Prompt: “Analyze this support ticket. Classify by: category (billing/technical/general), urgency (high/medium/low), sentiment (positive/neutral/negative). Then draft a helpful response using only the provided knowledge base.”
Template 5: Invoice Processing
Use Case: Extract data from invoices and enter into accounting system.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | Email with attachment or file upload |
| Extractor | GPT-4o Vision (read invoice details) |
| Validator | Check required fields, flag anomalies |
| Output | Create entry in QuickBooks/Xero + log to spreadsheet |
Key Prompt: “Extract from this invoice: vendor name, invoice number, date, line items (description, quantity, amount), subtotal, tax, total, payment terms.”
Template 6: Competitive Intelligence Monitor
Use Case: Track competitor activities and summarize changes.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | Daily schedule (8 AM) |
| Scrapers | Monitor competitor websites, social media, press releases |
| Analyzer | Compare to previous day, identify notable changes |
| Output | Daily digest email + trend dashboard update |
Key Prompt: “Compare today’s competitor intelligence to yesterday’s baseline. Highlight: 1) Pricing changes, 2) New product announcements, 3) Leadership changes, 4) Marketing campaign shifts.”
Template 7: Code Review Assistant
Use Case: Provide preliminary code review feedback before human review.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | New pull request opened |
| Analyzer | Claude Opus (security, performance, style review) |
| Checker | Verify tests pass, coverage adequate |
| Output | Comment on PR with findings and suggestions |
Key Prompt: “Review this code diff for: 1) Security vulnerabilities, 2) Performance issues, 3) Code style consistency, 4) Missing tests, 5) Documentation gaps. Be specific about line numbers.”
Template 8: Social Media Scheduler
Use Case: Generate and schedule social media content from content calendar.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | Weekly schedule or content calendar update |
| Generator | Create posts for each platform (Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram) |
| Image Creator | DALL-E or Midjourney for visual assets |
| Scheduler | Queue posts in Buffer/Hootsuite |
Key Prompt: “Create a week of social media posts for [brand]. Theme: [theme]. Include: mix of educational, promotional, and engaging content. Match each platform’s best practices for format and length.”
Template 9: Resume Screener
Use Case: Initial screening of job applications.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | New application submitted |
| Parser | Extract resume data (experience, skills, education) |
| Scorer | Match against job requirements |
| Output | Ranked candidate list with match scores and notes |
Key Prompt: “Score this resume against these job requirements: [requirements]. Provide: 1) Overall score (1-100), 2) Strengths alignment, 3) Gap areas, 4) Red flags, 5) Recommended interview questions.”
⚠️ Bias Warning: Always have humans make final hiring decisions. Use AI screening as a first filter only, and regularly audit for bias.
Template 10: Document Summarizer
Use Case: Summarize long documents for quick review.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | Document upload or email attachment |
| Chunker | Split into manageable sections |
| Summarizer | Claude for each chunk, then meta-summary |
| Output | Executive summary + key points email |
Key Prompt: “Create a 3-level summary of this document: 1) One-sentence TL;DR, 2) Executive summary (3-5 paragraphs), 3) Section-by-section key points.”
Template 11: Sales Call Analyzer
Use Case: Extract insights from sales call recordings.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | Call recording completed |
| Transcription | Whisper API |
| Analyzer | Extract objections, questions, next steps, sentiment |
| Output | CRM update + coaching notes for rep |
Key Prompt: “Analyze this sales call transcript. Extract: 1) Customer objections raised, 2) Competitor mentions, 3) Budget/timeline indicators, 4) Agreed next steps, 5) Deal score (1-10) with reasoning.”
Template 12: Daily Briefing Generator
Use Case: Personalized morning briefing with relevant news and tasks.
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Trigger | 6 AM daily |
| Aggregators | Calendar, email, news sources, project management tools |
| Synthesizer | Personalized summary and recommendations |
| Output | Email and/or audio summary via text-to-speech |
Key Prompt: “Create a 5-minute morning briefing including: 1) Today’s schedule with prep notes, 2) Priority emails needing attention, 3) Relevant industry news, 4) Top 3 tasks to focus on.”
Your Agentic Future Starts Now
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let me distill the key takeaways:
Key Principles
- Agentic AI transforms automation from rigid rules to intelligent decision-making
- The modern stack has five layers: Foundation Models → Frameworks → Platforms → Custom Interfaces → Standards (MCP)
- Choose your framework based on complexity: LangChain (simple) → LangGraph (stateful) → CrewAI (multi-agent)
- Platforms like Zapier and n8n democratize AI workflow creation for non-developers
- Custom GPTs and Claude Projects enable no-code AI specialists
- MCP is the emerging universal standard for AI-tool connectivity
- Measure ROI honestly: time saved, quality improved, new capabilities enabled
- Production systems need reliability, security, and observability
The December 2025 Landscape
We’re at an inflection point:
- Tools are mature: LangChain 1.0, LangGraph 1.0, n8n 2.0 all reached stable releases
- Standards are emerging: MCP and AAIF provide universal connectivity
- ROI is proven: 74% achieve returns in year one
The gap between AI-powered and traditional businesses is widening. The question isn’t “should I automate with AI?” but “how fast can I?”
Your Action Items
This week:
- Audit one workflow using the AUDIT framework. Pick something repetitive that takes 30+ minutes
- Build one simple automation with Zapier AI or n8n. Start with something low-stakes
- Create a Custom GPT or Claude Project for your specialty. Use it daily for two weeks
- Measure your time savings. Keep a log. The data will surprise you
What’s Next?
This article is part of our comprehensive AI Learning Series. Continue your journey:
- Previous: AI Agents - The Breakout Year of Autonomous AI
- Previous: Running LLMs Locally - Ollama, LM Studio, and the Open Source Revolution
- Next: The Future of LLMs - What’s Coming Next
The agentic future is here. The tools are ready. The only question is: what will you build?
Related Articles: